Online banking:
Online banking, is an electronic payment system that enables customers of a bank or other financial institution to conduct a range of financial transactions through the financial institution’s website. The online banking system will typically connect to or be part of the core banking system operated by a bank.

Automated supermarket checkouts:
Customers order their food online then collect from a drive-through, with bags pre-packed and loaded into the boot by supermarket employees. Payment is made online via an app or through a web browser.

Online classes:
They are academic classes (usually a college degree, but sometimes the term includes high school diplomas and non-degree certificate programs) that can be earned primarily or entirely through the use of an Internet-connected computer, rather than attending college in a traditional campus setting.

Online shopping:
Online shopping is The act of purchasing products or services over the Internet. Online shopping has grown in popularity over the years, mainly because people find it convenient and easy to bargain shop from the comfort of their home or office. One of the most enticing factor about online shopping, particularly during a holiday season, is it alleviates the need to wait in long lines or search from store to store for a particular item.

Online travel resources:
An OTA is a travel website that specializes in the sale of travel products to consumers. Some agencies sell a variety of travel products including flights, hotels, car rentals, cruises, activities, and packages. Other agencies, such as Viator, GetYourGuide, BeMyGuest, and others specialize in the sale of tours and activities. In all cases, the travel agency has an agency agreement with tour or activity suppliers to resell their products where the agency takes payment from the consumer and pays net rates to the supplier.

Malware: MALicious softWARE
Malware, or malicious software, is any program or file that is harmful to a computer user. Malware includes computer viruses, worms, Trojan horses and spyware. These malicious programs can perform a variety of functions, including stealing, encrypting or deleting sensitive data, altering or hijacking core computing functions and monitoring users’ computer activity without their permission.

Security Breaches:
A security breach is any incident that results in unauthorized access of data, applications, services, networks and/or devices by bypassing their underlying security mechanisms. A security breach occurs when an individual or an application illegitimately enters a private, confidential or unauthorized logical IT perimeter.
A security breach is also known as a security violation.

DoS: Denial of Service attacks
A denial-of-service attack is a security event that occurs when an attacker takes action that prevents legitimate users from accessing targeted computer systems, devices or other network resources.
Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks typically flood servers, systems or networks with traffic in order to overwhelm the victim resources and make it difficult or impossible for legitimate users to use them. While an attack that crashes a server can often be dealt with successfully by simply rebooting the system, flooding attacks can be more difficult to recover from.

Web Attacks:
A web threat is any threat that uses the World Wide Web to facilitate cybercrime. Web threats use multiple types of malware and fraud, all of which utilize HTTP or HTTPS protocols, but may also employ other protocols and components, such as links in email or IM, or malware attachments or on servers that access the Web. They benefit cybercriminals by stealing information for subsequent sale and help absorb infected PCs into botnets.

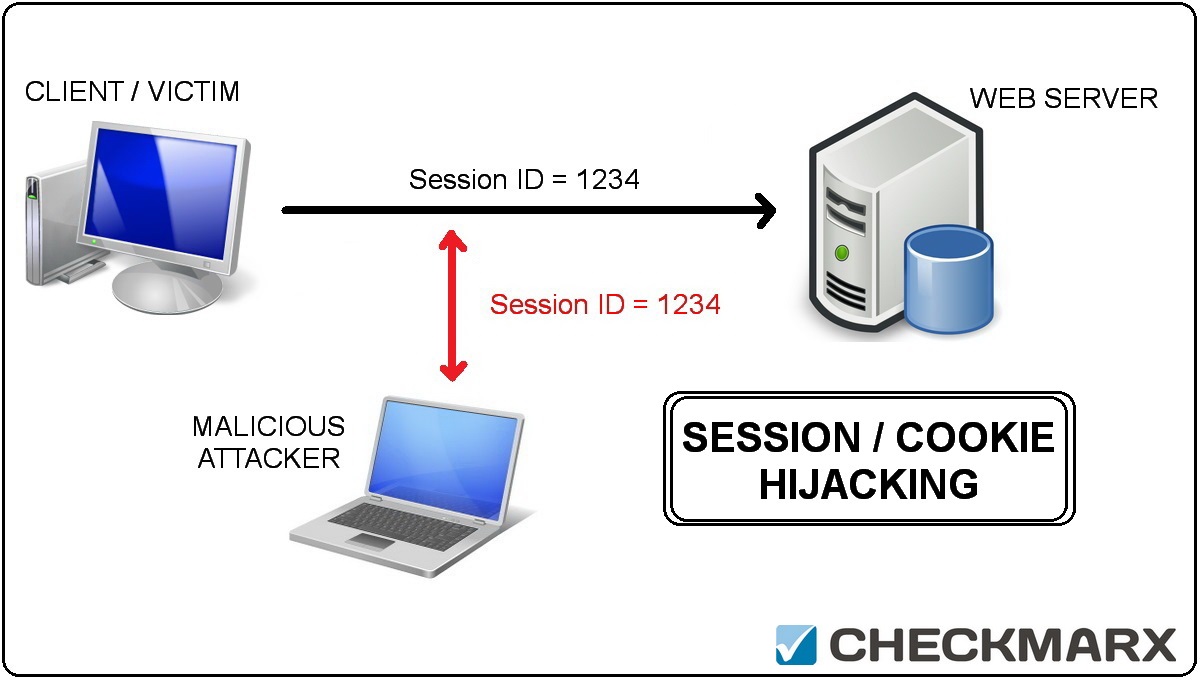
Session Hijacking
In computer science, session hijacking, sometimes also known as cookie hijacking is the exploitation of a valid computer session—sometimes also called a session key—to gain unauthorized access to information or services in a computer system. In particular, it is used to refer to the theft of a magic cookie used to authenticate a user to a remote server. It has particular relevance to web developers, as the HTTP cookies[1] used to maintain a session on many web sites can be easily stolen by an attacker using an intermediary computer or with access to the saved cookies on the victim’s computer (see HTTP cookie theft).
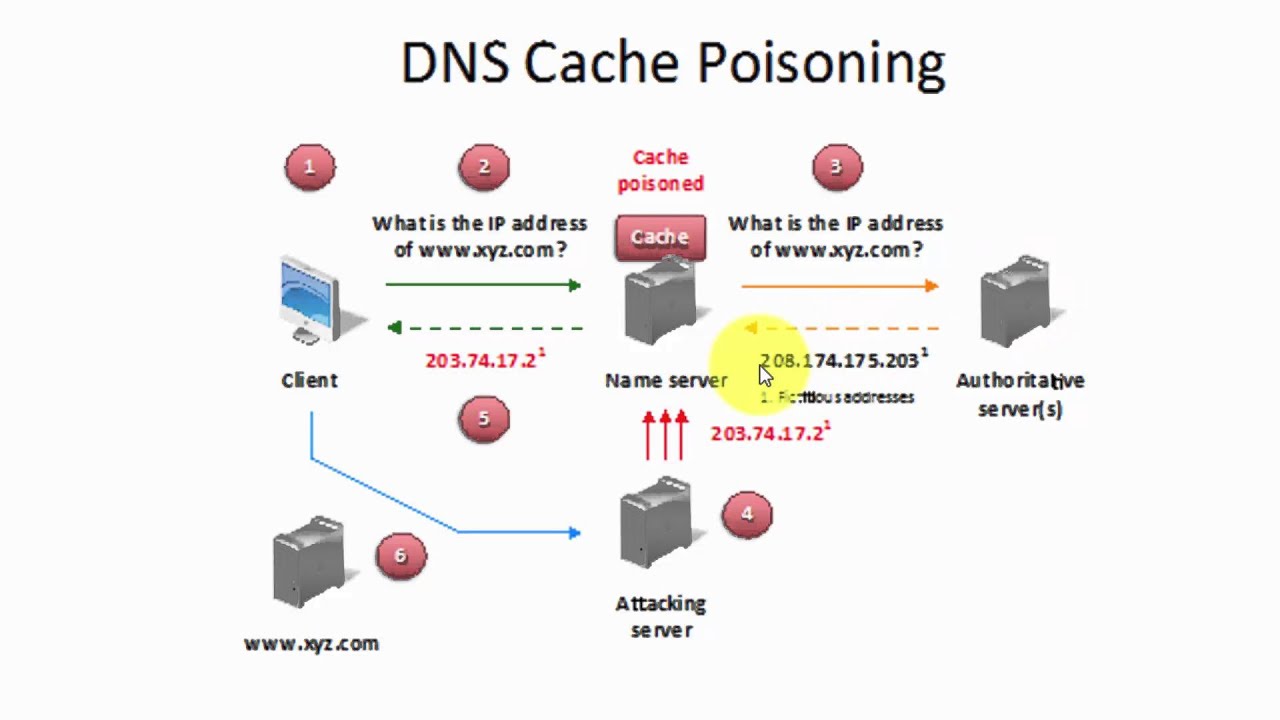
DNS Poisoning
DNS cache poisoning, also known as DNS spoofing, is a type of attack that exploits vulnerabilities in the domain name system (DNS) to divert Internet traffic away from legitimate servers and towards fake ones.
One of the reasons DNS poisoning is so dangerous is because it can spread from DNS server to DNS server. In 2010, a DNS poisoning event resulted in the Great Firewall of China temporarily escaping China’s national borders, censoring the Internet in the USA until the problem was fixed.
Virus
A computer virus is a type of malicious software program («malware») that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code. When this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be «infected» with a computer virus.

Trojan horse
In computing, a Trojan horse is a program that appears harmless, but is, in fact, malicious. Unexpected changes to computer settings and unusual activity, even when the computer should be idle, are strong indications that a Trojan is residing on a computer.

Spyware
Spyware is software that is installed on a computing device without the end user’s knowledge. Such software is controversial because even though it is sometimes installed for relatively innocuous reasons, it can violate the end user’s privacy and has the potential to be abused.

Logic Bomb
A logic bomb is a piece of code intentionally inserted into a software system that will set off a malicious function when specified conditions are met. For example, a programmer may hide a piece of code that starts deleting files (such as a salary database trigger), should they ever be terminated from the company.
Software that is inherently malicious, such as viruses and worms, often contain logic bombs that execute a certain payload at a pre-defined time or when some other condition is met. This technique can be used by a virus or worm to gain momentum and spread before being noticed. Some viruses attack their host systems on specific dates, such as Friday the 13th or April Fools’ Day. Trojans that activate on certain dates are often called «time bombs».

Hackers
A hacker is an individual who uses computer, networking or other skills to overcome a technical problem. The term hacker may refer to anyone with technical skills, but it often refers to a person who uses his or her abilities to gain unauthorized access to systems or networks in order to commit crimes. A hacker may, for example, steal information to hurt people via identity theft, damage or bring down systems and, often, hold those systems hostage to collect ransom.

White hats:
The term «white hat» in Internet slang refers to an ethical computer hacker, or a computer security expert, who specializes in penetration testing and in other testing methodologies to ensure the security of an organization’s information systems. Ethical hacking is a term coined by IBM meant to imply a broader category than just penetration testing. Contrasted with black hat, a malicious hacker, the name comes from Western films, where heroic and antagonistic cowboys might traditionally wear a white and a black hat respectively.

Black hats:
A black hat hacker (or black-hat hacker) is a hacker who «violates computer security for little reason beyond maliciousness or for personal gain».
The term was coined by hacker culture theorist Richard Stallman to contrast the exploitative hacker with the white hat hacker who hacks protectively by drawing attention to vulnerabilities in computer systems that require repair. The black hat/white hat terminology originates in the Western genre of popular American culture, in which black and white hats denote villainous and heroic cowboys respectively.
Black hat hackers are the stereotypically illegal hacking groups often portrayed in popular culture, and are «the epitome of all that the public fears in a computer criminal». Black hat hackers break into secure networks to destroy, modify, or steal data, or to make the networks unusable for authorized network users.

Gray hats:
The term «grey hat«, alternatively spelled as «greyhat» or «gray hat«, refers to a computer hacker or computer security expert who may sometimes violate laws or typical ethical standards, but does not have the malicious intent typical of a black hat hacker.
The term began to be used in the late 1990s, derived from the concepts of «white hat» and «black hat» hackers. When a white hat hacker discovers a vulnerability, they will exploit it only with permission and not divulge its existence until it has been fixed, whereas the black hat will illegally exploit it and/or tell others how to do so. The grey hat will neither illegally exploit it, nor tell others how to do so.

Script kiddies
In programming and hacking culture, a script kiddie or skiddie is an unskilled individual who uses scripts or programs developed by others to attack computer systems and networks and deface websites. It is generally assumed that most script kiddies are juveniles who lack the ability to write sophisticated programs or exploits on their own and that their objective is to try to impress their friends or gain credit in computer-enthusiast communities. However, the term does not relate to the actual age of the participant. The term is generally considered to be pejorative.

Sneakers
A security hacker is someone who seeks to breach defenses and exploit weaknesses in a computer system or network. Hackers may be motivated by a multitude of reasons, such as profit, protest, information gathering, challenge, recreation, or to evaluate system weaknesses to assist in formulating defenses against potential hackers. The subculture that has evolved around hackers is often referred to as the computer underground.

Ethical hackers
An ethical hacker is a computer and networking expert who systematically attempts to penetrate a computer system or network on behalf of its owners for the purpose of finding security vulnerabilities that a malicious hacker could potentially exploit.

Firewall
In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external network, such as the Internet.
Firewalls are often categorized as either network firewalls or host-based firewalls. Network firewalls filter traffic between two or more networks and run on network hardware. Host-based firewalls run on host computers and control network traffic in and out of those machines.

Proxy server
In computer networks, a proxy server is a server (a computer system or an application) that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity. Proxies were invented to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems. Today, most proxies are web proxies, facilitating access to content on the World Wide Web, providing anonymity and may be used to bypass IP address blocking.
Intrusion Detection System
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a system that monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and issues alerts when such activity is discovered. While anomaly detection and reporting is the primary function, some intrusion detection systems are capable of taking actions when malicious acitivity or anomalous traffic is detected, including blocking traffic sent from suspicious IP addresses.

